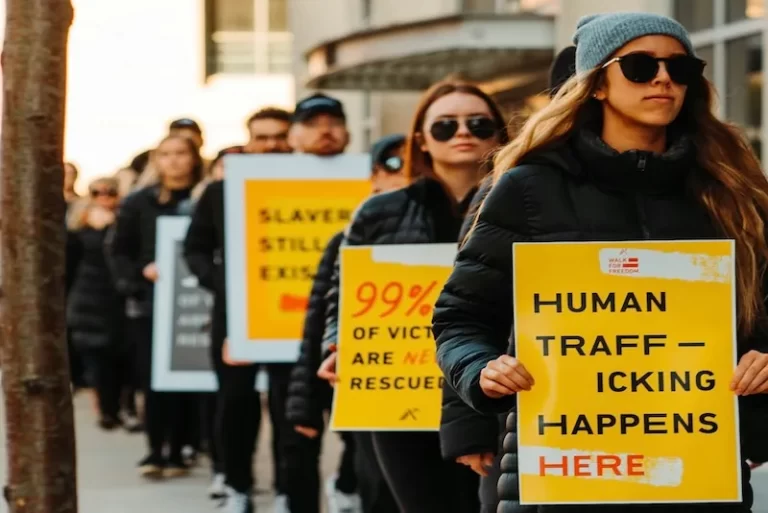
What is human trafficking?

Understanding human trafficking can be challenging for anyone. Human trafficking refers to the illegal trade and exploitation of people through force, fraud, or coercion. It involves the recruitment, transportation, transfer, harbouring, or receipt of individuals using deception, coercion, or abuse of power. The purpose is typically for forced labour, sexual exploitation, or other forms of exploitation.
Traffickers use various tactics to control and manipulate their victims, including physical violence, threats of harm to the victim or their families, psychological manipulation, false promises of a better life or job opportunities, and economic coercion.
Victims are often lured under false pretences, such as promises of well-paid jobs, educational opportunities, or marriage proposals, only to find themselves trapped in situations of exploitation and abuse.
Human trafficking is a form of modern-day slavery that deprives individuals of their freedom and dignity. It is a global issue affecting millions of people, including men, women, and children, and operates across various industries and regions worldwide.
Efforts to combat human trafficking involve raising awareness, strengthening legal frameworks, improving victim support and rehabilitation services, enhancing law enforcement capabilities, and addressing root causes such as poverty, inequality, and lack of opportunities. Recognising the signs of trafficking and
Trafficking happens everywhere
Human Trafficking in Cambodia
Human trafficking in Cambodia has become a pressing concern, particularly highlighted by recent warnings at airports targeting Korean and Taiwanese travellers. These warnings reflect the grim reality of trafficking in a region undergoing rapid transformation, such as Sihanoukville.
While the influx of Chinese investments has brought economic opportunities, it has also led to challenges, including an increase in illicit activities like human trafficking. It’s important to note that not all Chinese businesses are involved in such activities, but criminal elements exploit vulnerable populations.
Effective regulation, enforcement, and international cooperation are essential to combat these issues. Raising awareness among travellers, providing accurate information, and supporting efforts to protect vulnerable groups are key steps. Addressing human trafficking requires a multi-faceted approach involving governments, law enforcement agencies, NGOs, and communities.
As travellers and global citizens, staying informed and advocating for ethical practices can contribute to a safer and more just world.
Online Scams
A Growing Threat

Online scams have emerged as a significant global concern, manifesting in various forms such as phishing emails, fraudulent websites, and sophisticated schemes targeting unsuspecting individuals. Scammers often lure victims with promises of lucrative opportunities or manipulate them into divulging personal information for financial gain.
The prevalence of online scams underscores the importance of vigilance and awareness. Internet users should verify website authenticity, avoid sharing sensitive information, and use secure payment methods.
In Cambodia, efforts to combat online scams include stricter regulations, awareness campaigns, and enhanced cybersecurity infrastructure. As the digital landscape evolves, staying informed and cautious is essential to protect oneself from falling victim to these scams.
Child Trafficking
A Global Crisis

Child sex trafficking is a deeply disturbing form of abuse where individuals under 18 are coerced, sold, or exploited in commercial sexual activities. Traffickers exploit vulnerabilities such as poverty, lack of education, or unstable family environments.
In the Philippines, 1 in 100 children is sexually exploited online. A two-year study by The Sydney Herald revealed that Australian consumers play a significant role in funding this exploitation, with $1.3 million in suspicious transactions traced to Australia between 2020 and 2022.
Every child deserves protection and safety from such exploitation. Concerted global action is essential to eradicate this modern-day slavery.
Child Trafficking in Cambodia

Child traffickingChild trafficking in Cambodia remains a serious issue, exacerbated by lenient regulations governing NGOs and businesses. Some individuals exploit the guise of legitimate NGOs to perpetrate abuse, making robust oversight and accountability measures critical.
For those considering volunteering or supporting NGOs in Cambodia, thorough research is essential. Verify that the organisation operates transparently, adheres to ethical standards, and complies with Cambodian regulations. A crucial precaution is ensuring the NGO requires volunteers to provide a police report, which helps mitigate risks.
Strengthening regulatory frameworks, enhancing oversight mechanisms, and promoting ethical practices are vital to protecting children and communities from exploitation.
How can you recognise sex trafficking?

Sex rafficking is a hidden crime that often goes unnoticed. Unlike kidnapping or physical altercations, it doesn’t typically manifest in obvious ways. In Cambodia, undercover police monitor suspicious individuals, and organisations like APLE work tirelessly to combat trafficking.
Many victims may not realise they are being trafficked due to the manipulative tactics used by traffickers, such as grooming, emotional manipulation, and exploitation of trust. Raising awareness about these subtle indicators is crucial for identifying and supporting victims.
How do I report trafficking?
If you’re in the UK and suspect human trafficking, call the police:
- 999 for emergencies
- 101 for non-urgent matters
To remain anonymous, contact Crimestoppers at 0800 555 111. Alternatively, speak to a charity anonymously or call the National Human Trafficking Hotline at 1-888-373-7888. You can also chat online or fill out a form at humantraffickinghotline.org.
Trafficking Stats

Source: Polaris Project
Trafficking Statistics
Domestic (USA):
- The US is #1 globally for sex trafficking.
- Over 500,000 children go missing annually.
- 50% of victims are aged 12–15.
- 25% of child pornography is created by a neighbour or family member.
- Over 500,000 online sexual predators are active daily.
- 80% of child sex crimes begin on social media.
- 252,000 websites contain images or videos of child sexual abuse (2021).
Global:
- 27% of trafficking victims are children.
- Human trafficking is a $150 billion-a-year criminal enterprise.
These statistics highlight the urgent need for awareness, prevention, and intervention.
Takeaway
Prevention: The Best Approach

The best way to combat human trafficking is to prevent it before it occurs. For every individual rescued, traffickers often exploit others to take their place. Addressing root causes such as poverty, inequality, and lack of education is crucial.
Stay vigilant. Be cautious of individuals who constantly boast about their good deeds or portray themselves as saviours. Observe children who appear unusually quiet or overly attached to an adult, as these could be signs of grooming.
By staying informed and proactive, we can protect vulnerable individuals from exploitation. Preventing trafficking requires a community effort focused on awareness, education, and intervention.
If you’re in Cambodia, contact Child Safe or APLE for assistance.







